Type of Adverb
What Is an Adverb?
An adverb adds to a verb; it tells us how, how often, when, or where something was done. In other words, an adverb describes, modifies or provides more information about a verb in a sentence. So, if you said "I am going to quickly run to the store," the adverb in that sentence (quickly) would be modifying the verb "run."
Adverbs can be confused with adjectives, which also modify things. However, adjectives modify nouns and pronouns. If you said "I have a nice dog," then "dog" is the noun which is being modified by the adjective "nice".
On the other hand, if you said, "My dog quickly ate his dinner," the adverb "quickly" would modify the verb "ate."
In addition to verbs, adverbs also modify adjectives, other adverbs and word groups. So, when you say "I have the most beautiful dog," then "dog" is the noun, "beautiful" is the adjective describing the noun, and "most" is the adverb describing "beautiful."
Identifying Adverbs
You may have noticed a trend among adverbs; many, though not all, end in the letters "ly."
Knowing this can help you to quickly identify adverbs in sentences. However, remember that there are always exceptions, and some frequency adverbs, such as "always", "often", "sometimes", "seldom", and "never", do not follow this rule. Similarly, some words that end in "ly", such as "family" and "monopoly," are not adverbs.
Still, keeping an eye out for the "ly" ending can be a good tip to help you get started with successfully and correctly identifying adverbs.
List of Common Adverbs
A
abnormally
absentmindedly
accidentally
acidly
actually
adventurously
afterwards
almost
always
angrily
annually
anxiously
arrogantly
awkwardly
B
badly
bashfully
beautifully
bitterly
bleakly
blindly
blissfully
boastfully
boldly
bravely
briefly
brightly
briskly
broadly
busily
C
calmly
carefully
carelessly
cautiously
certainly
cheerfully
clearly
cleverly
closely
coaxingly
colorfully
commonly
continually
coolly
correctly
courageously
crossly
cruelly
curiously
D
daily
daintily
dearly
deceivingly
delightfully
deeply
defiantly
deliberately
delightfully
diligently
dimly
doubtfully
dreamily
E
easily
elegantly
energetically
enormously
enthusiastically
equally
especially
even
evenly
eventually
exactly
excitedly
extremely
F
fairly
faithfully
famously
far
fast
fatally
ferociously
fervently
fiercely
fondly
foolishly
fortunately
frankly
frantically
freely
frenetically
frightfully
fully
furiously
G
generally
generously
gently
gladly
gleefully
gracefully
gratefully
greatly
greedily
H
happily
hastily
healthily
heavily
helpfully
helplessly
highly
honestly
hopelessly
hourly
hungrily
I
immediately
innocently
inquisitively
instantly
intensely
intently
interestingly
inwardly
irritably
J
jaggedly
jealously
joshingly
joyfully
joyously
jovially
jubilantly
judgementally
justly
K
keenly
kiddingly
kindheartedly
kindly
kissingly
knavishly
knottily
knowingly
knowledgeably
kookily
L
lazily
less
lightly
likely
limply
lively
loftily
longingly
loosely
lovingly
loudly
loyally
M
madly
majestically
meaningfully
mechanically
merrily
miserably
mockingly
monthly
more
mortally
mostly
mysteriously
N
naturally
nearly
neatly
needily
nervously
never
nicely
noisily
not
O
obediently
obnoxiously
oddly
offensively
officially
often
only
openly
optimistically
overconfidently
owlishly
P
painfully
partially
patiently
perfectly
physically
playfully
politely
poorly
positively
potentially
powerfully
promptly
properly
punctually
Q
quaintly
quarrelsomely
queasily
queerly
questionably
questioningly
quicker
quickly
quietly
quirkily
quizzically
R
rapidly
rarely
readily
really
reassuringly
recklessly
regularly
reluctantly
repeatedly
reproachfully
restfully
righteously
rightfully
rigidly
roughly
rudely
S
sadly
safely
scarcely
scarily
searchingly
sedately
seemingly
seldom
selfishly
separately
seriously
shakily
sharply
sheepishly
shrilly
shyly
silently
sleepily
slowly
smoothly
softly
solemnly
solidly
sometimes
soon
speedily
stealthily
sternly
strictly
successfully
suddenly
surprisingly
suspiciously
sweetly
swiftly
sympathetically
T
tenderly
tensely
terribly
thankfully
thoroughly
thoughtfully
tightly
tomorrow
too
tremendously
triumphantly
truly
truthfully
U
ultimately
unabashedly
unaccountably
unbearably
unethically
unexpectedly
unfortunately
unimpressively
unnaturally
unnecessarily
utterly
upbeat
upliftingly
upright
upside-down
upward
upwardly
urgently
usefully
uselessly
usually
utterly
V
vacantly
vaguely
vainly
valiantly
vastly
verbally
very
viciously
victoriously
violently
vivaciously
voluntarily
W
warmly
weakly
wearily
well
wetly
wholly
wildly
willfully
wisely
woefully
wonderfully
worriedly
wrongly
Y
yawningly
yearly
yearningly
yesterday
yieldingly
youthfully
Z
zealously
zestfully
zestily
| A
abnormally
absentmindedly accidentally acidly actually adventurously afterwards almost always angrily annually anxiously arrogantly awkwardly | B
badly
bashfully beautifully bitterly bleakly blindly blissfully boastfully boldly bravely briefly brightly briskly broadly busily | C
calmly
carefully carelessly cautiously certainly cheerfully clearly cleverly closely coaxingly colorfully commonly continually coolly correctly courageously crossly cruelly curiously | D
daily
daintily dearly deceivingly delightfully deeply defiantly deliberately delightfully diligently dimly doubtfully dreamily | E
easily
elegantly energetically enormously enthusiastically equally especially even evenly eventually exactly excitedly extremely |
| F
fairly
faithfully famously far fast fatally ferociously fervently fiercely fondly foolishly fortunately frankly frantically freely frenetically frightfully fully furiously | G
generally
generously gently gladly gleefully gracefully gratefully greatly greedily | H
happily
hastily healthily heavily helpfully helplessly highly honestly hopelessly hourly hungrily | I
immediately
innocently inquisitively instantly intensely intently interestingly inwardly irritably | J
jaggedly
jealously joshingly joyfully joyously jovially jubilantly judgementally justly |
| K
keenly
kiddingly kindheartedly kindly kissingly knavishly knottily knowingly knowledgeably kookily | L
lazily
less lightly likely limply lively loftily longingly loosely lovingly loudly loyally | M
madly
majestically meaningfully mechanically merrily miserably mockingly monthly more mortally mostly mysteriously | N
naturally
nearly neatly needily nervously never nicely noisily not | O
obediently
obnoxiously oddly offensively officially often only openly optimistically overconfidently owlishly |
| P
painfully
partially patiently perfectly physically playfully politely poorly positively potentially powerfully promptly properly punctually | Q
quaintly
quarrelsomely queasily queerly questionably questioningly quicker quickly quietly quirkily quizzically | R
rapidly
rarely readily really reassuringly recklessly regularly reluctantly repeatedly reproachfully restfully righteously rightfully rigidly roughly rudely | S
sadly
safely scarcely scarily searchingly sedately seemingly seldom selfishly separately seriously shakily sharply sheepishly shrilly shyly silently sleepily slowly smoothly softly solemnly solidly sometimes soon speedily stealthily sternly strictly successfully suddenly surprisingly suspiciously sweetly swiftly sympathetically | T
tenderly
tensely terribly thankfully thoroughly thoughtfully tightly tomorrow too tremendously triumphantly truly truthfully |
| U
ultimately
unabashedly unaccountably unbearably unethically unexpectedly unfortunately unimpressively unnaturally unnecessarily utterly upbeat upliftingly upright upside-down upward upwardly urgently usefully uselessly usually utterly | V
vacantly
vaguely vainly valiantly vastly verbally very viciously victoriously violently vivaciously voluntarily | W
warmly
weakly wearily well wetly wholly wildly willfully wisely woefully wonderfully worriedly wrongly | Y
yawningly
yearly yearningly yesterday yieldingly youthfully | Z
zealously
zestfully zestily |
1 Adverbs of Degree
For adverbs that answer “how much” or to “what extent”, the are adverbs of degree. For example, they usually modify other verbs, adjectives or adverbs making them stronger or weaker.
These types of adverbs modify adjectives but not the other way around. In other words, adverbs can combine with other adverbs to put more emphasis on the verb. When you use ‘more’, ‘most’ and ‘least’, they can show degree when describing a verb.
ADVERBS OF DEGREE EXAMPLES:
- He’s very good at playing the piano.
- She’s almost always late arriving at school.
- It’s pretty interesting to see the history of China.
- The English test was extremely difficult.
- When he wears his running shoes, he moves more quickly among everyone.
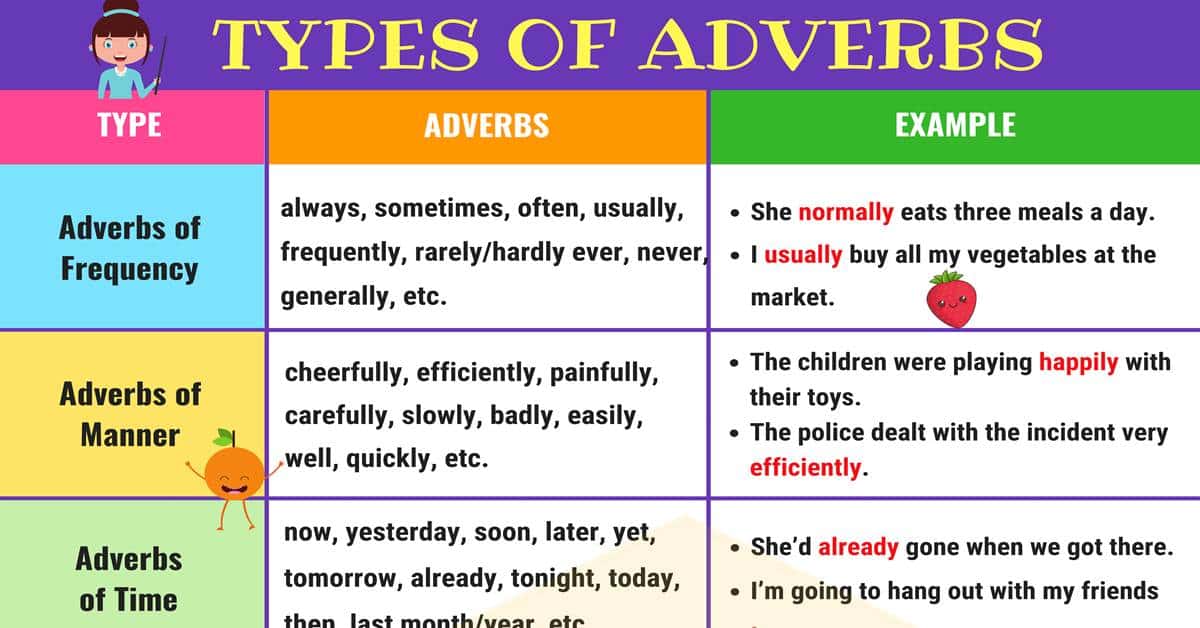
2 Adverbs of Frequency
Adverbs of frequency express “how often” something takes place. In other words, it explains the intensity of occurrence that an event happens. Adverbs of frequency are usually in this form: Subject + Adverb + Verb
| Adverb of Frequency | How Often |
| Never | 0% |
| Hardly Ever | 10% |
| Rarely | 20% |
| Seldom | 30% |
| Occasionally | 40% |
| Sometimes | 50% |
| Often | 60% |
| Frequently | 70% |
| Usually | 90% |
| Always | 100% |
In addition, adverbs like “daily”, “weekly”, “monthly” and “yearly” describe frequency. But these adverbs of frequency answer “how often” in a more specific way.
ADVERBS OF FREQUENCY EXAMPLES:
- I usually go to the gym on weekends.
- She always wake up at 7:00 am.
- The family rarely eat brown rice for dinner.
- I never take sick days.
3 Adverbs of Manner
Adverbs of manner express how something happens. In most cases for adverbs of manner, you can take an adjective and simply add -ly to form an adverb. For example, if you take take the sentence – “The cat is quick (adjective).”
Instead of describing a noun, an adverb describes or modifies a verb. In this case, the noun is the word ‘cat’. Because adverbs describe verbs, you need to add a verb in the sentence. For example, you can use the verb “to run” in this form – “The cat runs quickly.”
Adverbs of manner tell us the way or how to do something. However, not all adverbs end with -ly. For example, the words ‘fast’ and ‘well’ describe verbs but do not end in -ly.
ADVERBS OF MANNER EXAMPLES:
- The cat runs quickly.
- She plays the violin terribly.
- The horse moved fast.
- She plays the piano well.
4 Adverbs of Place
Adverbs of Place describe “where” an action takes place. In addition, we usually find adverbs of place after the main verb.
For example, “indoors”, “next week” and “still” all describe where something happens. Again, we often find these adverbs of place after a verb in a sentence.
ADVERBS OF PLACE EXAMPLES:
- If you want to see the hot air balloon, you will have to go outside.
- When she entered the classroom, she sat down.
- I searched everywhere but I couldn’t find him.
- He walks downstairs to meet his father.
5 Adverbs of Time
As with all adverbs, they tell us more about the verb. For adverbs of time, they tell us when the verb happened or will happen. For example, “afterwards”, “every day” and “recently’ are adverbs of time and describe “when”.
On the other hand, adverbs of time can describe the duration of an event occurs. Also, it can show when an action is complete.
ADVERBS OF TIME EXAMPLES:
- We’ll go to the festival tomorrow.
- Yesterday, we played in the basketball tournament.
- She’ll eventually finish studying and go to university.
- They ate popcorn and watched movies all day.
Other Example of adverbs
Adverb of time
An adverb of time tells us when something is done or happens. We use it at the beginning or at the end of a sentence. We use it as a form of emphasis when we place it at the beginning.
Adverbs of time include afterwards, already, always,immediately, last month, now, soon, then, and yesterday.
Examples:
- He collapsed and died yesterday.
- His factory was burned down a few months ago.
- Last week, we were stuck in the lift for an hour.
Adverb of place
An adverb of place tells us where something is done or happens. We use it after the verb, direct object or at the end of a sentence. Adverbs of place include words such as above, below, here, outside, over there, there, under, and upstairs.
Examples:
- We can stop here for lunch.
- The schoolboy was knocked over by a school bus.
- They rushed for their lives when fire broke out in the floor below.
Adverb of manner
An adverb of manner tells us how something is done or happens. Most adverbs of manner end in –ly such as badly, happily, sadly, slowly, quickly, and others that include well, hard and fast.
Examples:
- The brothers were badly injured in the fight.
- They had to act fast to save the others floating on the water.
- At the advanced age of 88, she still sang very well.
Adverb of degree
An adverb of degree tells us the level or extent that something is done or happens. Words of adverb of degree are almost, much, nearly, quite, really, so, too, very, etc.
Examples:
- It was too dark for us to find our way out of the cave. (Before adjective)
- The referee had to stop the match when it began to rain really heavily. (Before adverb)
- Her daughter is quite fat for her age.
- The accident victim nearly died from his injuries.
- After all these years, she is still feeling very sad about her father’s death.
Adverb of frequency
An adverb of frequency tells us how often something is done or happens. Words used as adverbs of frequency include again, almost, always, ever, frequently, generally, hardly ever, nearly, nearly always, never, occasionally, often, rarely, seldom, sometimes, twice, usually and weekly.
Examples:
- They were almost fifty when they got married.
- He hardly ever says something nice to his wife.
- While overseas, he frequently phoned home.
- She is not nearly always right although she thinks she is always right.
- He complained that she never smiled back.
- We only write to each other very occasionally..
- Peter seldom reads the Bible.
- Sometimeshe stays late in the office to complete his work..
- Our cat was bitten twice by the same dog.
- A man usually proposes marriage.
